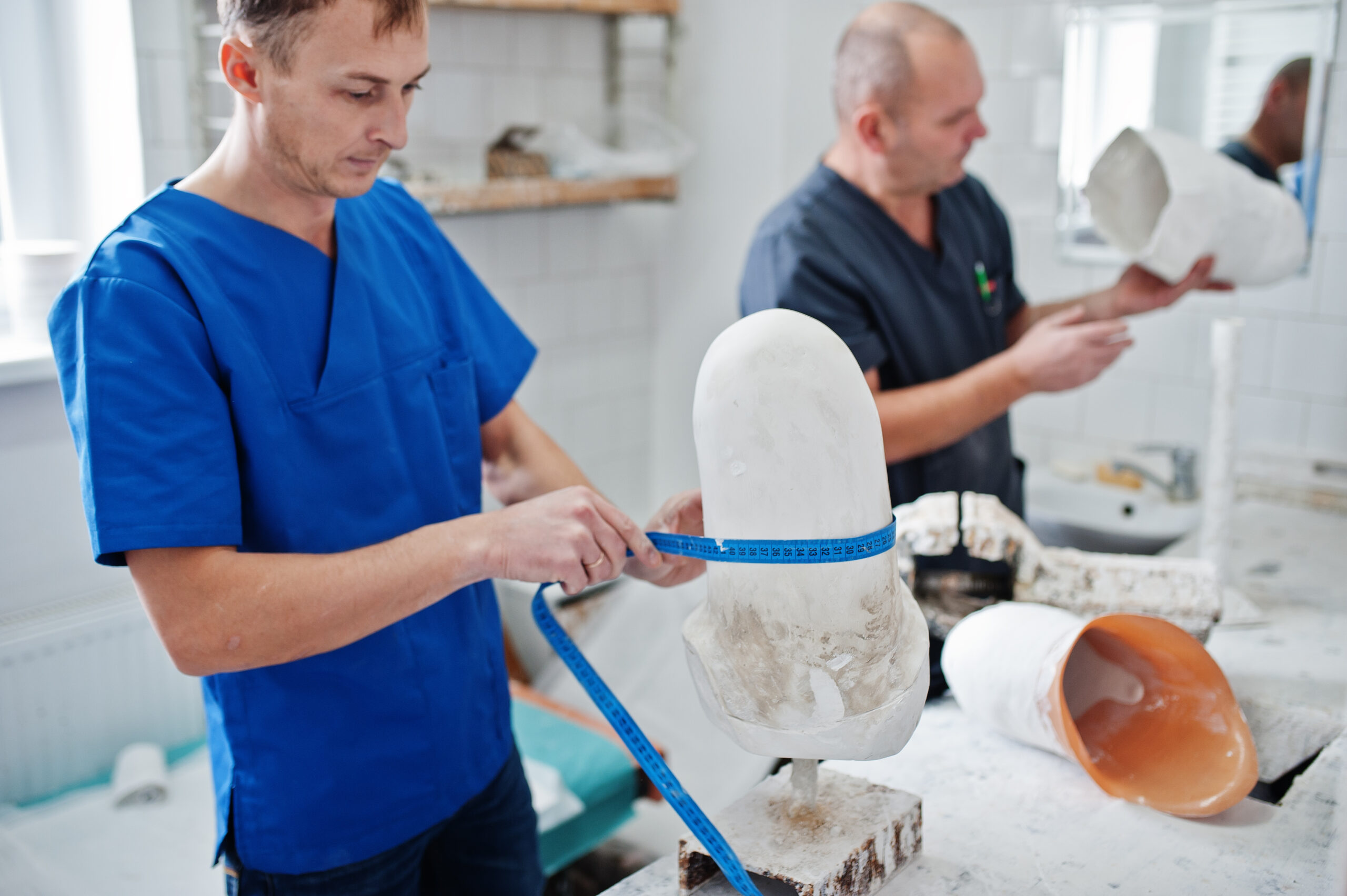
Two prosthetist man workers making prosthetic leg while working in laboratory.
For centuries, ceramics have been prized for their beauty, durability, and versatility. From ancient pottery to fine porcelain, ceramic craftsmanship has played a vital role in human culture and daily life. Today, however, ceramics are no longer confined to decorative or household uses. With the advancement of materials science, ceramics have evolved into highly engineered products that serve industries ranging from construction to aerospace.
One concept that captures this union of tradition and innovation is Sodiceram. At its core, Sodiceram represents a family of ceramic products that combine traditional craftsmanship with modern technological advancements. These products are not only beautiful but also designed with precision, durability, and performance in mind.
This article explores the meaning of Sodiceram, its history, its applications, benefits, challenges, and its potential role in shaping the future of materials.
What Is Sodiceram?
The term Sodiceram reflects an approach to ceramics that blends artisanal knowledge with scientific innovation. Unlike conventional ceramics, which are often limited to decorative or domestic functions, Sodiceram emphasizes functionality and technical performance.
These ceramic products are engineered to meet specific requirements such as:
-
High strength and durability
-
Resistance to heat, wear, and corrosion
-
Precision in design and application
-
Aesthetic versatility
In this sense, Sodiceram is not just about creating ceramics—it’s about redefining what ceramics can do in modern society.
The Roots of Sodiceram: Tradition Meets Science
Ceramics have a long history, dating back to prehistoric times. Early ceramics were made from natural clay, shaped by hand, and fired in rudimentary kilns. Over time, societies refined their techniques, leading to exquisite works such as Chinese porcelain, Islamic tiles, and European faience.
While traditional craftsmanship provided cultural value, the 20th century ushered in materials science, which transformed ceramics into advanced materials. Scientists discovered ways to manipulate ceramic structures at the microscopic level, giving rise to innovations such as:
-
Technical ceramics used in electronics and engineering
-
Bioceramics used in medical implants
-
Advanced composites for aerospace applications
Sodiceram builds on this dual heritage: it honors the artistry of ceramics while leveraging the precision and performance of scientific development.
Key Characteristics of Sodiceram
What sets Sodiceram apart from conventional ceramics? The following features define this family of products:
-
Durability
Sodiceram products are designed to withstand extreme conditions, from high temperatures to mechanical stress. -
Precision
With advanced manufacturing techniques, Sodiceram items can be produced with exact specifications, ensuring reliability in technical applications. -
Performance
Beyond aesthetics, Sodiceram emphasizes utility. Whether in construction, healthcare, or industry, these ceramics are built to deliver measurable results. -
Sustainability
Many Sodiceram products are eco-friendly, utilizing natural materials and long-lasting designs that reduce waste. -
Aesthetic Value
While performance is central, Sodiceram does not neglect visual appeal. Many products maintain the artistry that has always been central to ceramics.
Applications of Sodiceram
1. Architecture and Construction
In construction, Sodiceram materials are used for tiles, facades, and flooring. They combine elegance with durability, resisting wear, weather, and time. Advanced finishes and treatments allow architects to use Sodiceram in modern, sustainable building projects.
2. Industrial Applications
Technical Sodiceram ceramics serve industries requiring heat resistance, strength, and insulation. Examples include:
-
Furnace linings
-
Protective coatings
-
Wear-resistant machine parts
3. Healthcare
Bioceramic products derived from Sodiceram are increasingly common in medical applications, such as:
-
Dental implants
-
Bone replacements
-
Prosthetic components
These ceramics are biocompatible, ensuring safe interaction with the human body.
4. Energy Sector
Sodiceram materials support renewable energy through components for solar panels, wind turbines, and fuel cells. Their stability under extreme conditions makes them ideal for such applications.
5. Household and Lifestyle
From tableware to decorative pieces, Sodiceram also extends to everyday life. These products combine artistry with robustness, offering consumers items that are both practical and aesthetically pleasing.
6. Aerospace and Defense
Advanced Sodiceram composites are used in aerospace and defense for their lightweight strength and thermal resistance. These include heat shields, armor plating, and specialized components.
Benefits of Sodiceram
-
Longevity
The durability of Sodiceram ensures products last for decades, reducing replacement costs and waste. -
Versatility
With applications in industries as diverse as healthcare, energy, and design, Sodiceram demonstrates remarkable flexibility. -
Sustainability
Many Sodiceram products are environmentally friendly, supporting the global shift toward sustainable materials. -
Aesthetic-Functional Balance
Unlike purely technical ceramics, Sodiceram emphasizes the marriage of beauty and performance. -
Innovation Potential
With ongoing research in materials science, Sodiceram continues to evolve, pushing boundaries in design and application.
Challenges Facing Sodiceram
While promising, the Sodiceram concept also faces challenges:
-
Production Costs: Advanced ceramics require specialized equipment and processes, which can be costly.
-
Market Awareness: Many consumers and industries remain unaware of the full potential of Sodiceram.
-
Technical Limitations: Despite advances, ceramics can be brittle compared to metals or polymers.
-
Global Competition: As demand grows, competition in the ceramics market intensifies, requiring constant innovation.
Sodiceram and the Future of Materials
Looking ahead, Sodiceram is poised to play a central role in materials innovation. Future developments may include:
-
Nanostructured Ceramics
Enhancing performance at the nanoscale to achieve unprecedented strength and flexibility. -
Smart Ceramics
Integrating sensors and electronic capabilities into ceramic products for intelligent applications. -
Green Manufacturing
Adopting sustainable production methods to minimize environmental impact. -
3D Printing with Ceramics
Expanding design possibilities with additive manufacturing of Sodiceram components. -
Cross-Industry Collaborations
Bringing together designers, engineers, and scientists to unlock new uses for Sodiceram in global industries.
Why Sodiceram Matters Today
In a world increasingly focused on sustainability, performance, and innovation, Sodiceram embodies the convergence of tradition and modernity. It demonstrates how ancient knowledge can inform advanced solutions for today’s challenges.
From eco-friendly building materials to life-saving medical implants, Sodiceram is more than a product—it is a philosophy of design and engineering that values both artistry and utility.
Conclusion
Sodiceram represents a groundbreaking approach to ceramics, one that merges the timeless beauty of traditional craftsmanship with the power of modern materials science. By emphasizing durability, precision, and performance, Sodiceram products serve industries as diverse as architecture, healthcare, energy, and aerospace.
Though challenges remain in terms of cost, awareness, and technical development, the future of Sodiceram looks bright. Innovations in nanotechnology, smart materials, and sustainable manufacturing are likely to expand its reach and impact.
In the end, Sodiceram is not only about ceramics—it’s about envisioning a future where materials are smarter, stronger, and more sustainable. By honoring tradition while embracing innovation, Sodiceram shows how the past and present can unite to shape the future of design and industry.