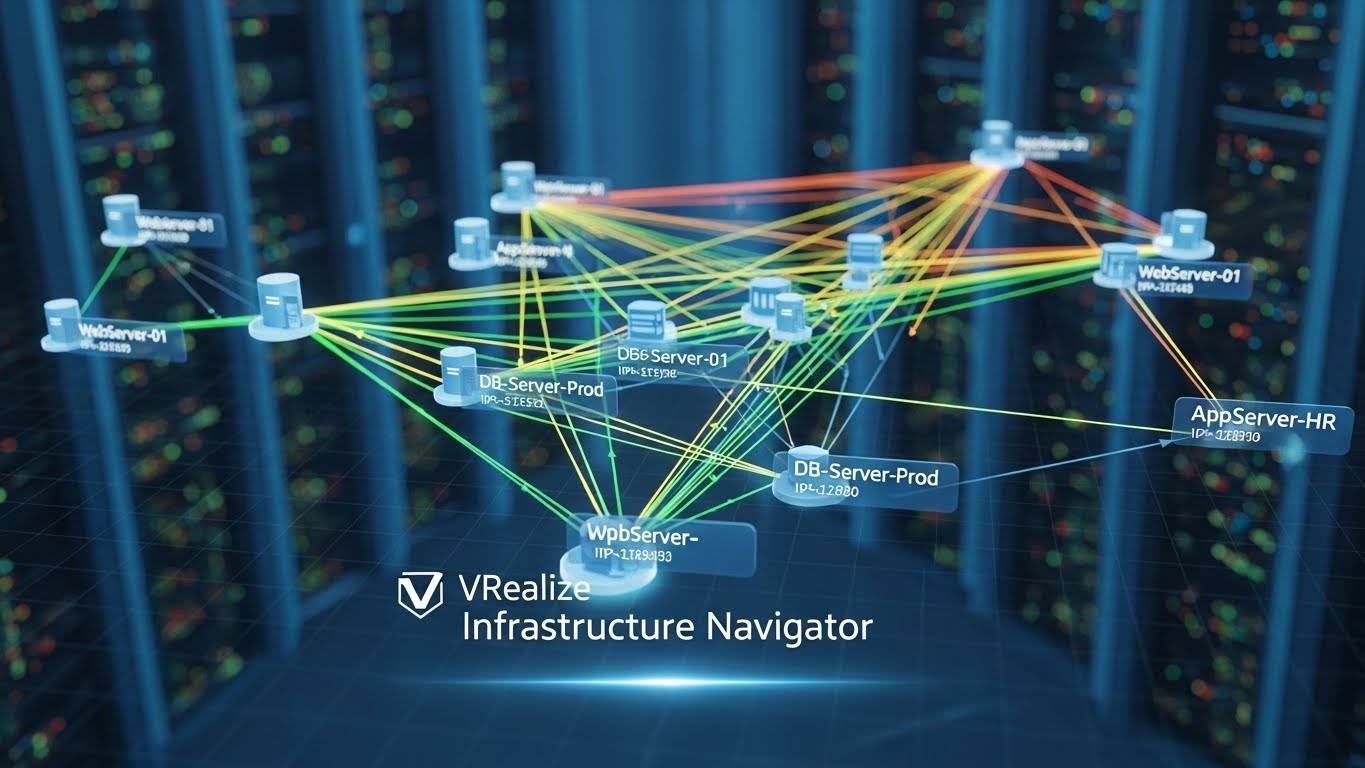
VRealize Infrastructure Navigator
In modern IT environments, understanding the intricate relationships between virtual machines (VMs) and the applications they host is critical for efficient management, troubleshooting, and optimization. VMware vRealize Infrastructure Navigator (VIN) was a specialized tool designed to simplify this process by providing deep insights into VM dependencies and network traffic. By visualizing application communications and mapping out the dependencies between VMs, VIN empowered IT administrators to maintain high-performing, reliable virtual environments.
What is vRealize Infrastructure Navigator?
VMware vRealize Infrastructure Navigator (VIN) is a virtual appliance that extends the capabilities of VMware vSphere. It provides IT administrators with a detailed understanding of application interactions and network communication within virtual environments. Unlike traditional monitoring tools that focus solely on the performance of individual VMs, VIN emphasizes relationships and dependencies between VMs, services, and applications. This capability allows administrators to see the bigger picture of how workloads interact within the data center.
VIN works by discovering applications running inside VMs and mapping their connections. It tracks communication between services, identifies which ports are being used, and provides a visual representation of these interactions. The tool essentially answers critical questions such as: Which VMs rely on each other? What services communicate over specific network ports? Are there bottlenecks or misconfigurations affecting application performance?
Key Features of VIN
VIN offered a range of features that made it an essential component for vSphere environments:
1. Application Dependency Mapping
One of the core functions of VIN was its ability to map dependencies between VMs. This feature allowed administrators to understand how different applications and services interact across the virtual infrastructure. For example, if a multi-tier application had a web server, application server, and database server running on separate VMs, VIN could visualize how each tier communicated. This mapping provided critical insights during troubleshooting, upgrades, or migrations, ensuring that changes to one VM did not unintentionally affect dependent services.
2. Network Traffic Visualization
VIN also tracked and visualized network traffic between VMs, highlighting the ports and protocols being used. By providing a clear view of communication flows, administrators could quickly identify unnecessary or suspicious network activity, optimize traffic paths, and enhance security. The visual representation made it easier to pinpoint misconfigured firewalls or unoptimized communication patterns, which might otherwise remain hidden in complex virtual environments.
3. Integration with vSphere
VIN was designed to integrate seamlessly with VMware vSphere, allowing administrators to access its capabilities directly from the vSphere Web Client. This integration meant that administrators could analyze VM dependencies in the context of the overall virtual infrastructure, without the need for separate tools or consoles. It provided a unified view of both VM performance and application interactions.
4. Simplified Troubleshooting
By visualizing the dependencies and communication patterns of applications, VIN greatly simplified troubleshooting. When an application experienced performance issues, administrators could trace the flow of traffic and dependencies to identify the root cause quickly. For instance, if a database server was underperforming, VIN could show which VMs were generating traffic toward it, revealing potential overloads or misconfigured connections.
5. Support for Multi-Tier Applications
Modern applications often consist of multiple layers or tiers, each with specific responsibilities and dependencies. VIN’s ability to automatically discover these multi-tier applications and map their internal communications was particularly valuable. It reduced the manual effort required to document dependencies and ensured that no hidden connections were overlooked.
Benefits of Using VIN
Implementing vRealize Infrastructure Navigator brought several advantages to IT operations:
-
Enhanced Visibility: Administrators gained clear insight into how VMs and applications interacted, making it easier to manage complex virtual environments.
-
Improved Troubleshooting: By pinpointing communication paths and dependencies, VIN reduced the time needed to diagnose issues.
-
Optimized Performance: Understanding traffic patterns helped identify bottlenecks and optimize resource allocation.
-
Better Planning: When planning upgrades, migrations, or capacity expansions, VIN provided essential data to minimize risk and downtime.
-
Security Awareness: Visualizing which VMs communicated over which ports allowed administrators to detect unauthorized access or unusual traffic patterns.
Use Cases of VIN
VIN was widely used across various scenarios in enterprise IT:
1. Data Center Migrations
During migrations, understanding VM dependencies is critical to avoid disrupting services. VIN’s mapping capabilities enabled administrators to plan migrations with confidence, ensuring that dependent VMs were moved together and communication remained intact.
2. Application Performance Optimization
By visualizing traffic flows, administrators could identify which VMs generated the most traffic and which services were underperforming. This information allowed them to optimize configurations and resource allocation.
3. Troubleshooting and Root Cause Analysis
VIN accelerated root cause analysis by showing real-time and historical VM communication patterns. Administrators could quickly trace problems to the exact VM, service, or network port causing issues.
4. Security and Compliance Monitoring
VIN helped monitor network traffic for unusual patterns, such as unauthorized access attempts or unexpected inter-VM communications. This capability was valuable for maintaining security standards and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Limitations
While VIN provided significant benefits, it also had some limitations:
-
Legacy Tool: VIN is considered a legacy solution, and VMware has gradually moved its functionality into newer tools like vRealize Operations (vROps).
-
Resource Overhead: Running VIN as a virtual appliance required additional resources, which could be a concern in resource-constrained environments.
-
Limited Real-Time Analytics: While VIN offered visualization and dependency mapping, its real-time analytics capabilities were not as advanced as newer monitoring solutions.
Conclusion
vRealize Infrastructure Navigator was a powerful tool for understanding VM dependencies and network traffic within VMware vSphere environments. Its ability to map application relationships, visualize communication flows, and simplify troubleshooting made it an essential solution for administrators managing complex virtual infrastructures. Although it has largely been replaced by more modern tools within the vRealize suite, VIN’s principles continue to influence how IT teams approach VM dependency mapping and traffic analysis today.
By leveraging the insights provided by VIN, organizations could optimize application performance, enhance security, and plan infrastructure changes with confidence. For IT administrators tasked with managing large-scale virtual environments, understanding the dependencies and traffic patterns of VMs remains a fundamental aspect of maintaining a healthy, efficient, and secure data center.