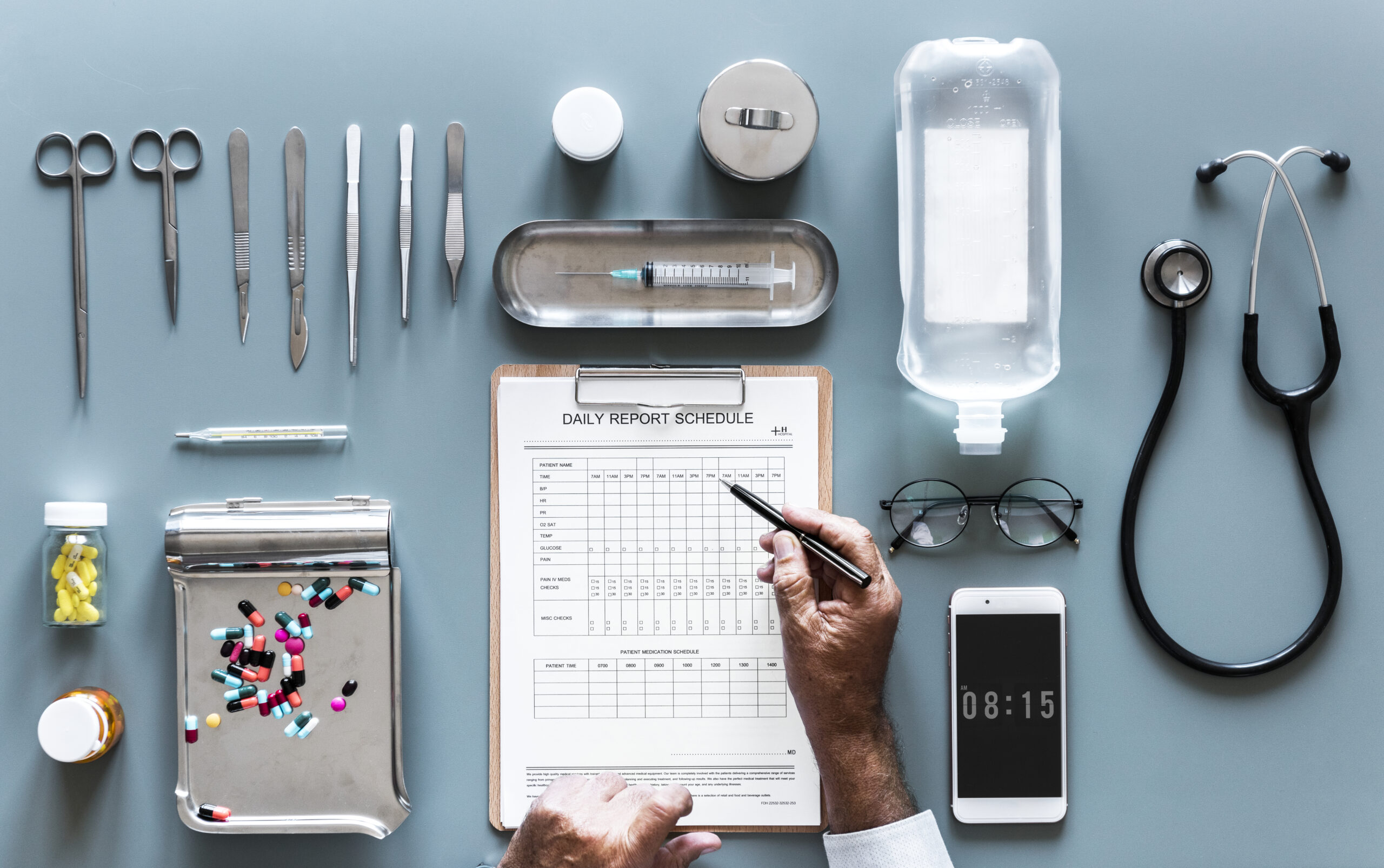
In the world of medicine, precision and attentiveness are everything. Every sound, pulse, and rhythm inside the human body can tell a story about a person’s health. One of the most timeless instruments that allows medical professionals to interpret these internal cues is the fonendi. Though it may not be a household word like “stethoscope,” the fonendi serves a similar and equally vital purpose: it is a diagnostic instrument used for auscultation—listening to the internal sounds of a patient’s body.
Over time, fonendi devices have evolved from simple listening tools into sophisticated diagnostic instruments that aid doctors, nurses, and medical students in evaluating the condition of the heart, lungs, and other organs. In this article, we will explore what fonendi is, how it works, its historical evolution, types, uses, and its importance in modern healthcare.
What Is a Fonendi?
A fonendi is a medical diagnostic instrument designed for auscultation, the practice of listening to the sounds produced within the body, primarily the heart, lungs, and intestines. The term itself comes from the Greek roots “phono-,” meaning sound, and “endi-,” related to internal or within.
The fonendi helps medical professionals detect abnormalities in internal sounds that could indicate underlying conditions. For instance, irregular heartbeats, wheezing in the lungs, or abnormal bowel sounds can all be picked up and analyzed using this instrument.
While many people use “stethoscope” as a general term, the fonendi represents a more refined or specialized version. It focuses on sound clarity and acoustic precision, helping practitioners make more accurate assessments.
Historical Background
The origins of the fonendi can be traced back to the early 19th century, when René Laennec, a French physician, invented the first stethoscope in 1816. His design was a simple wooden tube, but it revolutionized the way doctors examined patients. Over the years, this tool evolved through numerous stages—first becoming the binaural stethoscope with two earpieces, and later being enhanced with acoustic and electronic technology.
The fonendi emerged as a modern adaptation—integrating improved acoustic design, noise filtering, and ergonomic comfort. The term is commonly used in certain regions and languages to describe advanced stethoscopes or auscultation devices that provide superior sound fidelity and sensitivity.
How Fonendi Works
The working principle of the fonendi revolves around sound transmission. Here’s how it functions:
-
Sound Capture – When the diaphragm or bell of the fonendi is placed against a patient’s skin, it picks up vibrations caused by internal sounds, such as heartbeats or breath sounds.
-
Sound Transmission – These vibrations travel through the tubing system to the earpieces, where the medical practitioner can hear them clearly.
-
Sound Amplification (in some models) – Advanced or electronic fonendi models can amplify weak sounds, making subtle murmurs or faint lung noises easier to detect.
There are generally two key components used in most fonendi designs:
-
The Diaphragm: Used to listen to high-frequency sounds, such as normal heartbeats and breath sounds.
-
The Bell: Used for low-frequency sounds, such as abnormal heart murmurs or bowel sounds.
This dual-function design allows clinicians to adapt quickly to different diagnostic needs with a single instrument.
Types of Fonendi
Modern fonendi instruments can be categorized into several types depending on their design and technology:
-
Acoustic Fonendi:
This is the most traditional type, relying purely on sound conduction through hollow tubes. It is lightweight, reliable, and doesn’t require batteries. -
Electronic Fonendi:
These advanced versions amplify sound electronically and may include noise cancellation, digital recording, or Bluetooth connectivity. They are ideal for noisy environments and telemedicine applications. -
Pediatric Fonendi:
Designed for children and infants, these fonendi models have smaller diaphragms and softer ear tips for comfort and better sound precision. -
Cardiology Fonendi:
Used by cardiologists, these instruments are fine-tuned to capture subtle cardiac murmurs or irregular rhythms with higher fidelity.
Each of these types serves a unique purpose, allowing healthcare providers to choose the most suitable fonendi for their specific field and patient needs.
Applications in Medicine
The fonendi is a multifunctional diagnostic tool that plays a vital role in almost every branch of healthcare. Here are some of its primary uses:
-
Cardiology:
-
Detecting heart murmurs, arrhythmias, or abnormal valve sounds.
-
Monitoring heartbeat intensity and rhythm.
-
-
Pulmonology:
-
Listening to lung sounds for signs of wheezing, crackles, or decreased breath sounds that could indicate pneumonia, asthma, or COPD.
-
-
Gastroenterology:
-
Assessing bowel sounds to detect intestinal obstruction or motility issues.
-
-
Pediatrics and Neonatology:
-
Evaluating heart and lung sounds in infants and children where precision is critical.
-
-
General Practice:
-
Routine checkups to ensure the proper functioning of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems.
-
Importance in Modern Healthcare
Despite technological advancements such as ultrasound and digital imaging, the fonendi remains one of the most indispensable tools in clinical medicine. Its simplicity, immediacy, and portability make it invaluable in a wide range of settings—from hospitals and clinics to rural healthcare and emergency response units.
Here are some reasons why the fonendi remains essential:
-
Instant Diagnosis: It provides immediate feedback during physical examinations.
-
Cost-Effective: Unlike electronic imaging tools, fonendi devices are affordable and accessible.
-
Non-Invasive: No discomfort or risk is involved in auscultation.
-
Training Tool: It helps medical students develop essential diagnostic listening skills.
Additionally, the modern evolution of fonendi instruments into digital or AI-integrated devices enhances their diagnostic capabilities. Some advanced versions even allow for sound visualization, digital recording, and remote monitoring, which are crucial in telemedicine and digital health applications.
Maintenance and Care
For accurate performance and hygiene, proper care of the fonendi is vital. Here are a few guidelines:
-
Regular Cleaning: Use alcohol wipes or mild soap to clean the diaphragm, bell, and tubing.
-
Avoid Extreme Temperatures: Excessive heat or cold can damage the tubing and affect sound transmission.
-
Earpiece Maintenance: Replace earpieces periodically to maintain comfort and hygiene.
-
Check Seals and Tubing: Ensure airtight connections for optimal acoustic quality.
By following these maintenance tips, practitioners can extend the lifespan of their fonendi and ensure consistent diagnostic performance.
The Future of Fonendi
As healthcare embraces digital transformation, the future of fonendi lies in smart integration. Upcoming models are being designed with features such as:
-
Digital recording and playback for teaching or consultation.
-
Wireless data transmission for remote diagnosis.
-
AI-based sound analysis to detect abnormalities automatically.
These innovations will not only enhance diagnostic accuracy but also democratize access to quality healthcare in underserved areas.
Conclusion
The fonendi stands as a symbol of medical tradition and innovation—a simple yet powerful tool that bridges human intuition and scientific precision. From the first heartbeat a doctor hears to the subtle sounds of recovery, the fonendi remains an irreplaceable companion in the journey of healing.
Its legacy continues to grow as new technologies elevate its capabilities, proving that even in an age of digital medicine, the act of listening remains one of the most profound diagnostic arts.